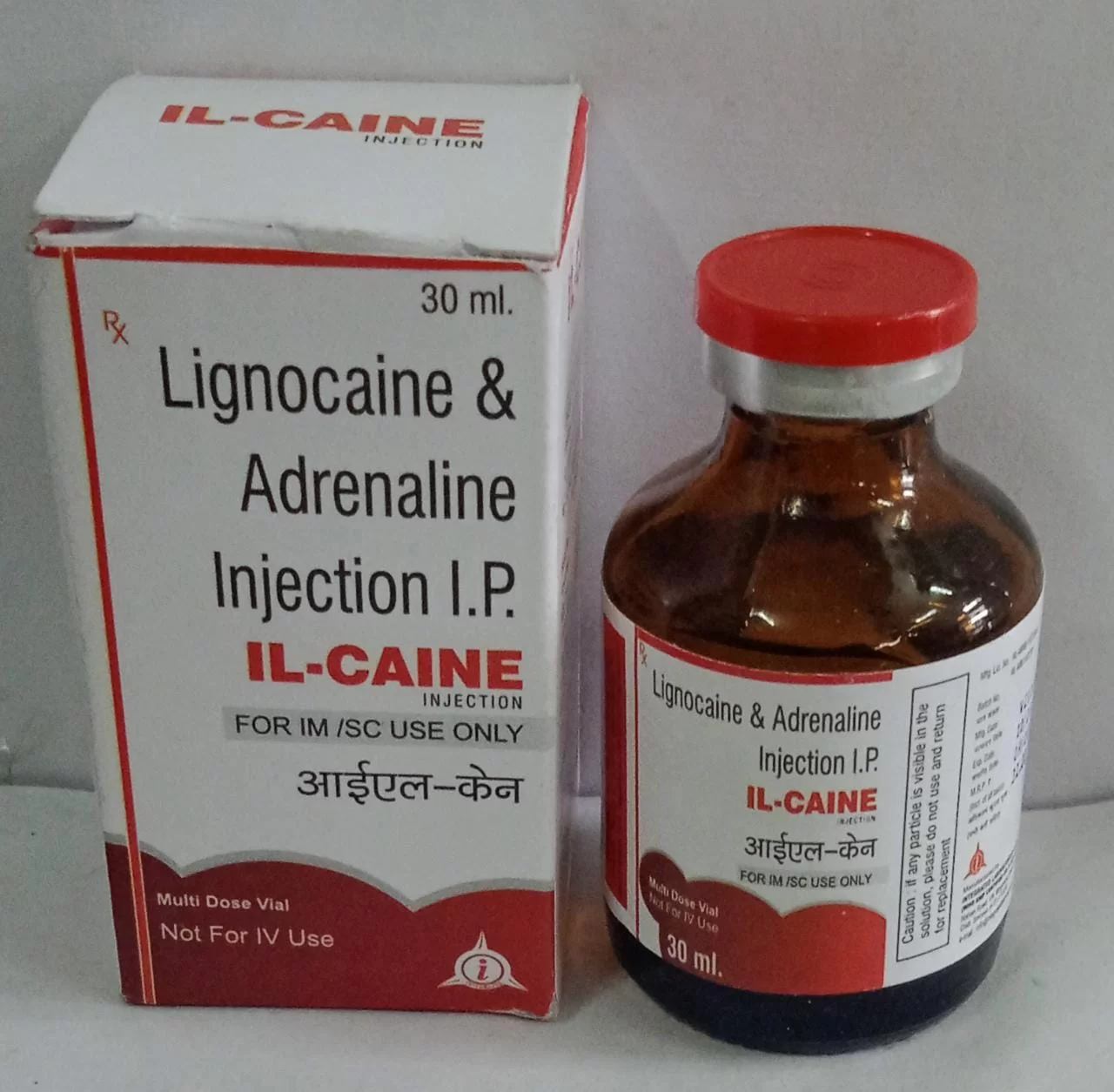
Lignocaine Adrenaline Injection
Lignocaine (Lidocaine) Hydrochloride: A local anesthetic. Lignocaine Adrenaline Injection, Local Anesthetic Injection, Anesthetic Solution with Epinephrine
Adrenaline (Epinephrine): A vasoconstrictor.
A typical formulation might contain:
Lignocaine 1% or 2% (10–20 mg/mL)
Adrenaline 1:100,000 or 1:200,000 (0.01–0.005 mg/mL)
Mechanism of Action
Lignocaine:
Blocks voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve membranes.
Prevents nerve impulse conduction, causing local anesthesia.
Adrenaline:
Stimulates α-adrenergic receptors causing vasoconstriction.
Local Anesthetic Injection
This:
Prolongs anesthetic effect by reducing blood flow.
Reduces bleeding at the site.
Delays systemic absorption of lignocaine (reduces toxicity).
Indications / Uses
Local Anesthesia:
Dental procedures
Minor surgical interventions
Skin and soft tissue infiltration
Obstetric and gynecologic procedures (with caution)
ENT, ophthalmologic, and orthopedic uses
Nerve Blocks:
Peripheral nerve blocks
Epidural (careful formulation without preservatives)
Lignocaine Adrenaline Injection
Hemostasis:
Used where bleeding control is essential due to vasoconstriction effect
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to amide-type local anesthetics or adrenaline.
Peripheral vascular disease (risk of tissue ischemia)
Areas supplied by end arteries (e.g., fingers, toes, ears, nose, penis)
Severe hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, or ischemic heart disease
Hyperthyroidism or pheochromocytoma
Local Anesthetic Injection
Dosage and Administration
Dosage (Adults)
Route Lignocaine Max Dose (with Adrenaline)
Infiltration / Nerve Block 7 mg/kg (not to exceed 500 mg total)
Always adjust for weight, age, and comorbidities. Anesthetic Solution with Epinephrine
Onset: 2–5 minutes
Duration: 1–3 hours (longer with adrenaline)
Example for dental block:
2% lignocaine with 1:100,000 adrenaline – 1.8–3.6 mL per block
Pediatric Dose:
3–5 mg/kg (lignocaine with adrenaline) – more conservative approach
Side Effects / Adverse Reactions
From Lignocaine:
CNS toxicity (dizziness, tinnitus, seizures)
Cardiovascular depression (hypotension, bradycardia, arrhythmias)
Lignocaine Adrenaline Injection
From Adrenaline:
Palpitations
Anxiety or restlessness
Hypertension
Cardiac arrhythmias
Precautions
Monitor cardiac function and vital signs during administration.
Avoid repeated dosing in short intervals.
Ensure aspiration before injection to avoid intravascular injection.
Use with caution in elderly or those with hepatic impairment.
Be wary in patients on beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, or MAO inhibitors.
Drug Interactions
Beta-blockers: Risk of hypertensive reaction
MAO inhibitors / TCAs: Potentiate adrenaline effects
Antiarrhythmic drugs: May increase lignocaine toxicity
Lidocaine Epinephrine Injection
Special Warnings
Avoid using in terminal vascular field areas (e.g., digits, penis, ears) due to ischemic necrosis risk.
Not recommended for IV regional anesthesia (Bier block) due to risk of systemic toxicity.
Storage
Store between 15–25°C
Protect from light
Discard any discolored solution or if precipitate forms
Available Forms
1% or 2% Lignocaine with 1:100,000 or 1:200,000 Adrenaline
Packaging: Ampoules or vials (e.g., 2 mL, 5 mL, 10 mL)
Benefits
Enhanced anesthetic duration
Reduced bleeding in operative field
Decreased systemic lignocaine toxicity
Risks
Ischemia in extremities
Cardiotoxicity if overdosed
Drug interactions and CNS effects
Lidocaine Epinephrine Injection
Veterinary Use
Used similarly for local anesthesia in small animals and sometimes large animals for minor procedures.
Avoid in end-artery areas (ears, tails, claws).
Dosage should be strictly weight-adjusted.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.